
Solar power generation
Solar power generation is a method of generating electricity that takes advantage of a phenomenon of electricity being generated when light strikes silicon semiconductors and other materials. Since we will never run out of sunlight no matter how much we use, it is widely accepted all over the world, and is the most installed renewable energy in Japan. Renewable Japan is dedicated to development, power generation, operation and management of solar power plants.
Features of solar power generation
-
It is a clean and environmentally friendly power generation method that does not produce exhaust gas or CO2 while generating power as long as the sun is present with no risk of resource depletion.
-
Basically, power cannot be generated at night when the sun is not shining, but more power can be generated during the day when electricity demand is relatively high.
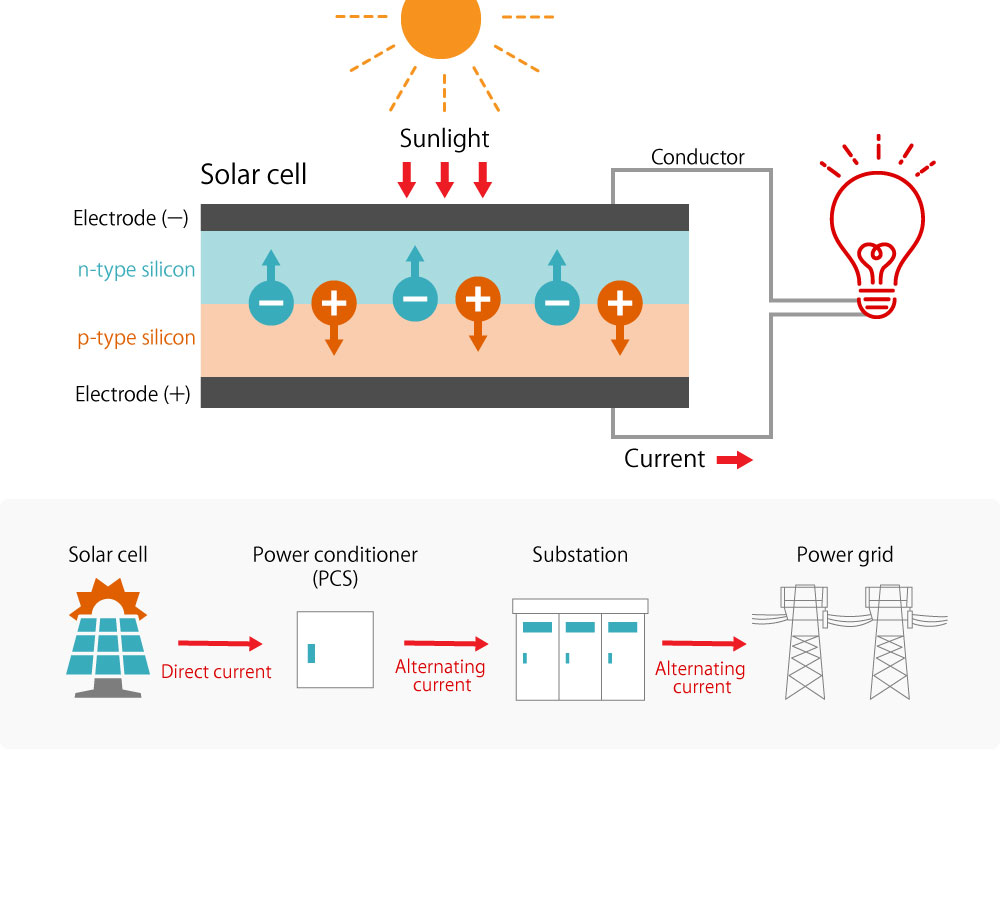
How solar power generation works
Silicon solar cells, which are the mainstream today, have a structure with two types of semiconductors having different electrical properties, known as “n-type” and “p-type” semiconductors, in layers. When these cells are exposed to sunlight, electrons (-) and holes (+) are generated. The electrons are attracted to the “n-type” semiconductor side (front side) and the holes to the “p-type” semiconductor side (back side), which causes electric current to flow when a load, such as a bulb or motor, is connected to the electrodes on the front and back sides.
How a solar power plant is built
From searching for potential sites, to the management after commercial operation, we conduct all the phases for a project.
planning
- Land selection and negotiation
- Field surveys
- Basic design of the power plant
Development
- Consultation with local authorities on administrative permissions
- Consultation with utility companies on grid connection
- Presentation of the business plan to the local community
Construction
- Detailed design of power plant
- Civil work (Landscaping and construction of retention basin, etc.)
- Electrical work (Installation of solar panels, power conditioners and substation equipment,etc.)
Operation
- Various inspections and test runs
- Establish a business management systems, including operation and maintenance
Solar power plant
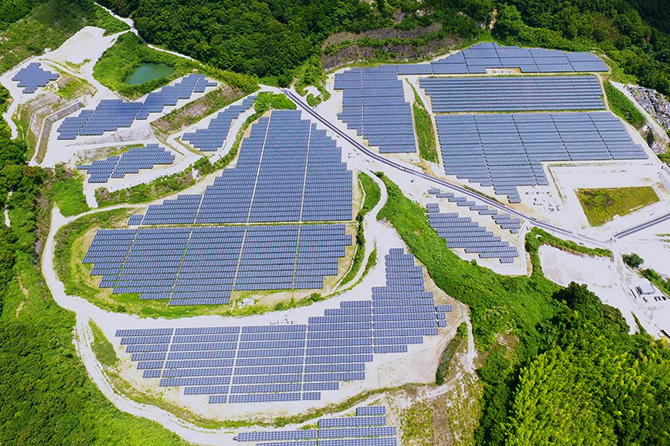

Shizuoka
- Capacity
-
11.3MW
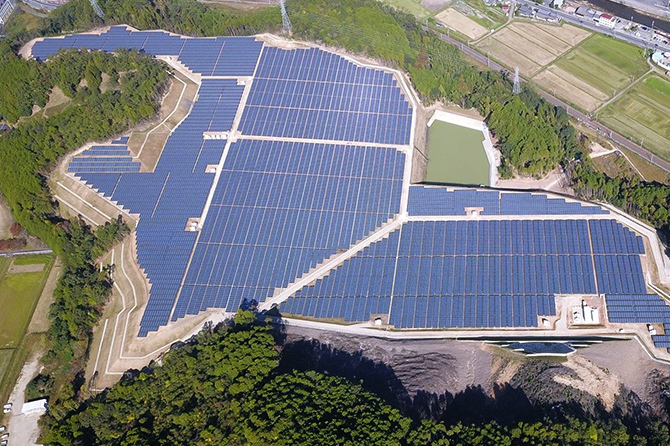

Kyoto
- Capacity
-
14.5MW

Mie
- Capacity
-
10.4MW